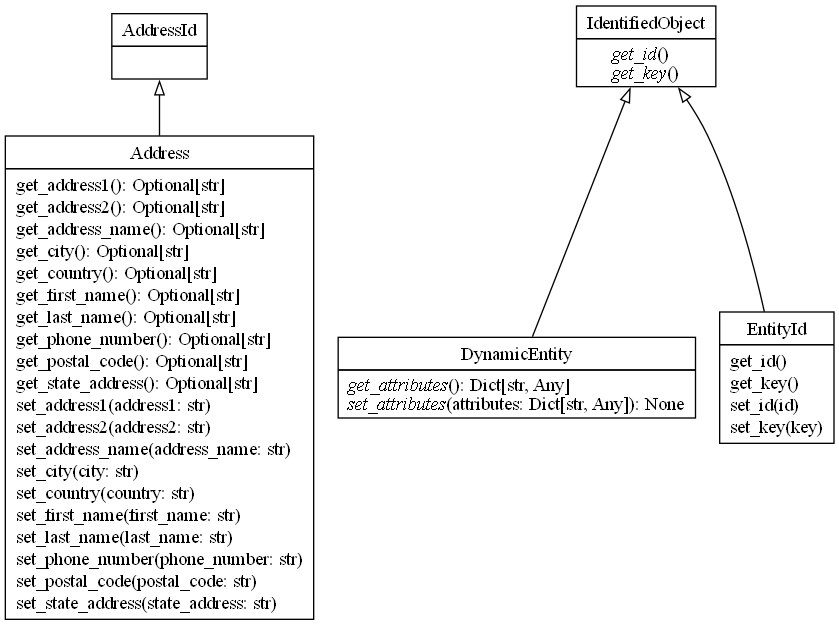
Base
Class Diagrams
Key Components
-
DynamicEntity
-
Defines a dynamic, attribute-driven entity capable of holding runtime-configurable key-value pairs.
-
Useful for extending predefined entities with flexible, non-static attributes to address unique business requirements.
-
EntityId
-
Provides a universal mechanism for uniquely identifying entities using UUID or custom string-based keys.
-
Forms the foundation for consistent and reusable entity identification across the MachC ecosystem.
-
IdentifiedObject
-
Introduces an interface that standardizes unique identification for domain objects.
-
Ensures that all identifiable entities implement coherent getters for UUIDs and secondary keys.
-
Dynamic Attributes Management
-
Enables support for customizable runtime attributes through a consistent attribute-container design pattern.
-
Allows entities like products or orders to store additional key-value properties beyond static attributes.
-
Utilities for Entity Abstraction
-
Additional utilities are provided to simplify common functionalities like serialization, mapping identifiers, and handling dynamic characteristics.
- Fosters reusability, eliminating duplication in domain-specific entities.
Clean Architecture Alignment
The MachC Base Domain Library adheres to Clean Architecture principles by providing:
- Core Abstractions: Ensuring that essential entities and interfaces remain independent of business-specific layers.
- Reusability: These base entities are designed to be reused across various domains, minimizing redundancy.
- Extensibility: Offers a robust framework for extending the foundational elements into higher-level domain-specific entities, such as products, orders, and users.
Why Use the MachC Base Domain Library?
- Scalability:
Built to serve as the core for large-scale applications, enabling seamless integration and extension as business demands grow.
- Consistency Across Domains:
The use of shared identifiers and standardized entity structures ensures uniformity, reducing complexity in multi-domain systems.
- Flexibility:
With DynamicEntity and related abstractions, developers have the freedom to enhance entities at runtime without modifying core logic.
- Foundation for Domain-Specific Libraries:
Acts as the groundwork upon which all other domain libraries (e.g., User, Product, Order) are built, ensuring a cohesive architecture.
Use Cases
- Universal Identifiers: Use
EntityIdandIdentifiedObjectto standardize unique identification across various domains. - Runtime Flexibility: Use
DynamicEntityto add key-value pairs dynamically for entities like products, users, or orders. - Interoperability: Ensures integration between multiple domain libraries while maintaining independence and modularity.